
|
[The final semicolon in class types has been accepted before.]
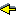
The table below shows the relative precedences and associativity of operators and non-closed type constructions. The constructions with higher precedences come first.
| Operator | Associativity |
| Type constructor application | – |
| # | – |
| * | – |
| -> | right |
| as | – |
Type expressions denote types in definitions of data types as well as in type constraints over patterns and expressions.
The type expression ' ident stands for the type variable named ident. The type expression _ stands for an anonymous type variable. In data type definitions, type variables are names for the data type parameters. In type constraints, they represent unspecified types that can be instantiated by any type to satisfy the type constraint. In general the scope of a named type variable is the whole top-level phrase where it appears, and it can only be generalized when leaving this scope. Anonymous variables have no such restriction. In the following cases, the scope of named type variables is restricted to the type expression where they appear: 1) for universal (explicitly polymorphic) type variables; 2) for type variables that only appear in public method specifications (as those variables will be made universal, as described in section 6.9.1); 3) for variables used as aliases, when the type they are aliased to would be invalid in the scope of the enclosing definition (i.e. when it contains free universal type variables, or locally defined types.)
The type expression ( typexpr ) denotes the same type as typexpr.
The type expression typexpr1 -> typexpr2 denotes the type of functions mapping arguments of type typexpr1 to results of type typexpr2.
label-name : typexpr1 -> typexpr2 denotes the same function type, but the argument is labeled label.
? label-name : typexpr1 -> typexpr2 denotes the type of functions mapping an optional labeled argument of type typexpr1 to results of type typexpr2. That is, the physical type of the function will be typexpr1 option -> typexpr2.
The type expression typexpr1 * … * typexprn denotes the type of tuples whose elements belong to types typexpr1, … typexprn respectively.
Type constructors with no parameter, as in typeconstr, are type expressions.
The type expression typexpr typeconstr, where typeconstr is a type constructor with one parameter, denotes the application of the unary type constructor typeconstr to the type typexpr.
The type expression (typexpr1,…, typexprn) typeconstr, where typeconstr is a type constructor with n parameters, denotes the application of the n-ary type constructor typeconstr to the types typexpr1 through typexprn.
The type expression typexpr as ' ident denotes the same type as typexpr, and also binds the type variable ident to type typexpr both in typexpr and in other types. In general the scope of an alias is the same as for a named type variable, and covers the whole enclosing definition. If the type variable ident actually occurs in typexpr, a recursive type is created. Recursive types for which there exists a recursive path that does not contain an object or polymorphic variant type constructor are rejected, except when the -rectypes mode is selected.
If ' ident denotes an explicit polymorphic variable, and typexpr denotes either an object or polymorphic variant type, the row variable of typexpr is captured by ' ident, and quantified upon.
|
[The tag-spec-first change excludes the grammar production that permits a polymorphic variant type containing only one type expression, which was not accepted by the compiler anyway. The leading & in full tag specifications has been accepted before.]
Polymorphic variant types describe the values a polymorphic variant may take.
The first case is an exact variant type: all possible tags are known, with their associated types, and they can all be present. Its structure is fully known.
The second case is an open variant type, describing a polymorphic variant value: it gives the list of all tags the value could take, with their associated types. This type is still compatible with a variant type containing more tags. A special case is the unknown type, which does not define any tag, and is compatible with any variant type.
The third case is a closed variant type. It gives information about all the possible tags and their associated types, and which tags are known to potentially appear in values. The exact variant type (first case) is just an abbreviation for a closed variant type where all possible tags are also potentially present.
In all three cases, tags may be either specified directly in the `tag-name [of typexpr] form, or indirectly through a type expression, which must expand to an exact variant type, whose tag specifications are inserted in its place.
Full specifications of variant tags are only used for non-exact closed types. They can be understood as a conjunctive type for the argument: it is intended to have all the types enumerated in the specification.
Such conjunctive constraints may be unsatisfiable. In such a case the corresponding tag may not be used in a value of this type. This does not mean that the whole type is not valid: one can still use other available tags.
An object type < [method-type { ; method-type }] > is a record of method types.
Each method may have an explicit polymorphic type: { ' ident }+ . typexpr. Explicit polymorphic variables have a local scope, and an explicit polymorphic type can only be unified to an equivalent one, where only the order and names of polymorphic variables may change.
The type < {method-type ;} .. > is the type of an object whose method names and types are described by method-type1, …, method-typen, and possibly some other methods represented by the ellipsis. This ellipsis actually is a special kind of type variable (called row variable in the literature) that stands for any number of extra method types.
The type # class-path is a special kind of abbreviation. This abbreviation unifies with the type of any object belonging to a subclass of class class-path. It is handled in a special way as it usually hides a type variable (an ellipsis, representing the methods that may be added in a subclass). In particular, it vanishes when the ellipsis gets instantiated. Each type expression # class-path defines a new type variable, so type # class-path -> # class-path is usually not the same as type (# class-path as ' ident) -> ' ident.
Use of #-types to abbreviate polymorphic variant types is deprecated. If t is an exact variant type then #t translates to [< t], and #t[> `tag1 …` tagk] translates to [< t > `tag1 …` tagk]
There are no type expressions describing (defined) variant types nor record types, since those are always named, i.e. defined before use and referred to by name. Type definitions are described in section 6.8.1.


